Field Types
Base Data Types
Section titled “Base Data Types”Anybuild uses the incredible PostgreSQL database for managing data.
Postgres includes a rich set of datatypes - see table below
| Name | Aliases | Description |
|---|---|---|
| bigint | int8 | signed eight-byte integer |
| bigserial | serial8 | autoincrementing eight-byte integer |
| bit [ (n) ] | fixed-length bit string | |
| bit varying [ (n) ] | varbit [ (n) ] | variable-length bit string |
| boolean | bool | logical Boolean (true/false) |
| box | rectangular box on a plane | |
| bytea | binary data (“byte array”) | |
| character [ (n) ] | char [ (n) ] | fixed-length character string |
| character varying [ (n) ] | varchar [ (n) ] | variable-length character string |
| cidr | IPv4 or IPv6 network address | |
| circle | circle on a plane | |
| date | calendar date (year, month, day) | |
| double precision | float8 | double precision floating-point number (8 bytes) |
| inet | IPv4 or IPv6 host address | |
| integer | int, int4 | signed four-byte integer |
| interval [ fields ] [ (p) ] | time span | |
| json | textual JSON data | |
| jsonb | binary JSON data, decomposed | |
| line | infinite line on a plane | |
| lseg | line segment on a plane | |
| macaddr | MAC (Media Access Control) address | |
| macaddr8 | MAC (Media Access Control) address (EUI-64 format) | |
| money | currency amount | |
| numeric [ (p, s) ] | decimal [ (p, s) ] | exact numeric of selectable precision |
| path | geometric path on a plane | |
| pg_lsn | PostgreSQL Log Sequence Number | |
| pg_snapshot | user-level transaction ID snapshot | |
| point | geometric point on a plane | |
| polygon | closed geometric path on a plane | |
| real | float4 | single precision floating-point number (4 bytes) |
| smallint | int2 | signed two-byte integer |
| smallserial | serial2 | autoincrementing two-byte integer |
| serial | serial4 | autoincrementing four-byte integer |
| text | variable-length character string | |
| time [ (p) ] [ without time zone ] | time of day (no time zone) | |
| time [ (p) ] with time zone | timetz | time of day, including time zone |
| timestamp [ (p) ] [ without time zone ] | date and time (no time zone) | |
| timestamp [ (p) ] with time zone | timestamptz | date and time, including time zone |
| tsquery | text search query | |
| tsvector | text search document | |
| txid_snapshot | user-level transaction ID snapshot (deprecated; see pg_snapshot) | |
| uuid | universally unique identifier | |
| xml | XML data |
Custom Datatypes
Section titled “Custom Datatypes”Data Definition Layer >> Field Types >> New Field Type
Custom Datatypes are a very useful feature to support Data Integrity and accuracy. They enable the Base Data Types to be further constrained by defining additional checks such as min max values or length checks or format checks.
e.g. An ISO Currency Code should be 3 Upper Case letters.
Below is an example Regex to define this check
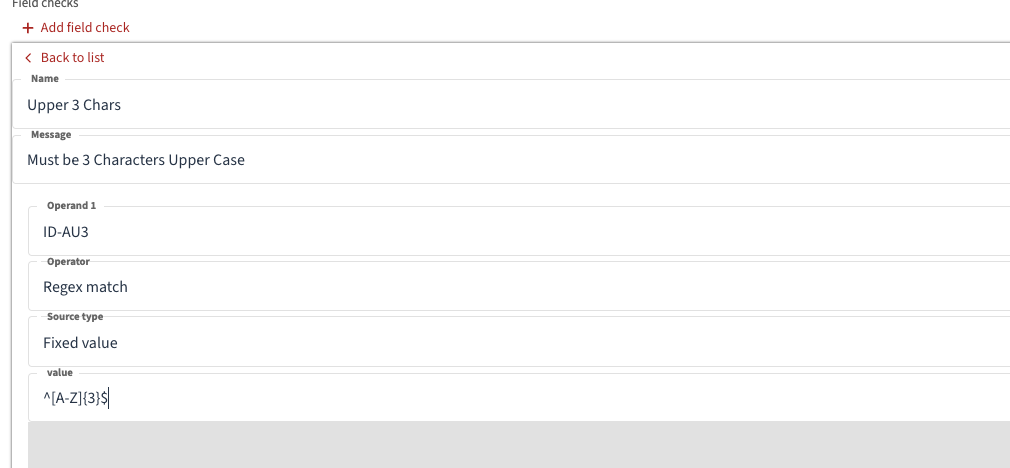
For more complex check examples see Help
e.g. to check Credit Card format.
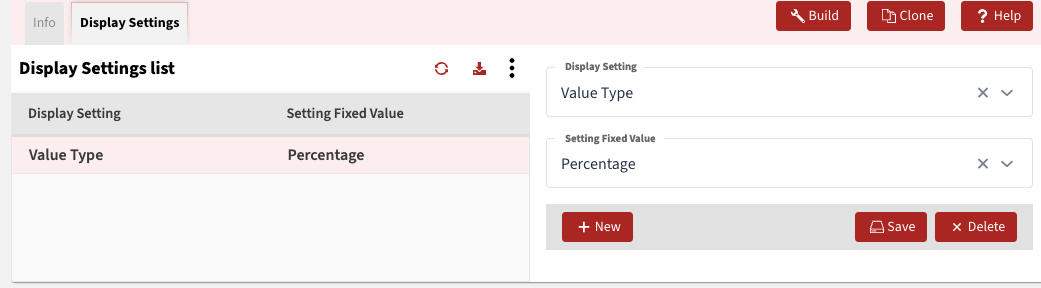
Field Type Formats
Section titled “Field Type Formats”Display Settings tab you can set custom formats e.g. percentage below